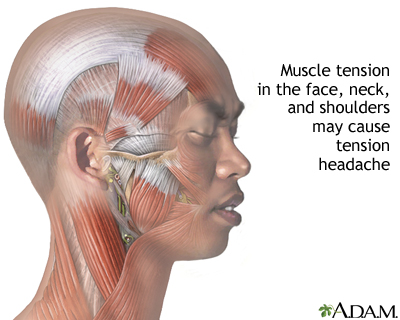
What Is a Tension Headache?
A tension headache—also called a stress headache—is the most common type of primary headache. It causes a dull, aching pain or pressure around the head, often described as a tight band squeezing the head.
While uncomfortable, it is usually not disabling and doesn’t come with nausea or visual disturbances like migraines.
🧠 Key Features of Tension Headache
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Pain quality | Dull, aching, squeezing or pressure-like |
| Location | Both sides of the head (bilateral), forehead, temples, or back of head |
| Intensity | Mild to moderate |
| Duration | 30 minutes to several hours, or even days |
| Activity impact | Not worsened by movement (unlike migraine) |
| Other symptoms | Possible mild light or sound sensitivity |
| No nausea or aura | Differentiates from migraines |
📅 Types of Tension Headache
| Type | Characteristics |
|---|---|
| Episodic | Occurs less than 15 days a month |
| Chronic | Occurs 15 or more days per month for 3+ months |
⚠️ Common Causes of Tension Headaches
Tension headaches are thought to result from muscle tension and stress, but the exact mechanism isn’t fully understood. Likely contributors include:
1. Stress (Mental or Emotional)
- Anxiety
- Work or relationship stress
- Depression
2. Muscle Tension
- Neck and shoulder tightness
- Poor posture
- Jaw clenching or teeth grinding (bruxism)
3. Physical Strain
- Eye strain (e.g., from screens)
- Long hours of reading or computer work
- Fatigue or overexertion
4. Sleep Issues
- Insomnia
- Irregular sleep patterns
- Poor sleep posture
5. Environmental Factors
- Noise
- Bright lights
- Poor ergonomics at work
6. Caffeine Withdrawal or Overuse
- Either too much or suddenly cutting back on caffeine
🩺 Diagnosis
Tension headaches are diagnosed clinically, meaning:
- Based on symptoms
- No specific test is required
- CT or MRI only if unusual symptoms appear (e.g., sudden severe pain, neurological signs)
💊 Treatment Options
Acute (Relief of Individual Headaches)
| Medication | Notes |
|---|---|
| Acetaminophen | First-line for mild to moderate pain |
| Ibuprofen/Naproxen | NSAIDs reduce pain and inflammation |
| Aspirin | May help but not suitable for everyone |
⚠️ Avoid overuse: Regular use of pain meds can cause medication-overuse headaches (rebound headaches).
Chronic or Frequent Headaches – Preventive Strategies
1. Medications
- Amitriptyline (low-dose): Most commonly prescribed preventive medication
- Other antidepressants: If depression is a contributing factor
- Muscle relaxants: In select cases
2. Lifestyle Changes
- Regular sleep schedule
- Hydration
- Stress management (e.g., mindfulness, CBT)
- Ergonomic improvements (desk posture, screen height)
3. Physical Therapies
- Massage therapy
- Stretching and neck/shoulder exercises
- Heat therapy (for muscle tension)
✅ Key Takeaways
- Tension headaches are common and typically not serious, but can be chronic and disruptive.
- They are often triggered by stress, poor posture, and muscle tension.
- Treatment focuses on pain relief, prevention, and lifestyle adjustments.
Would you like a comparison table between tension, migraine, and cluster headaches to better distinguish them?