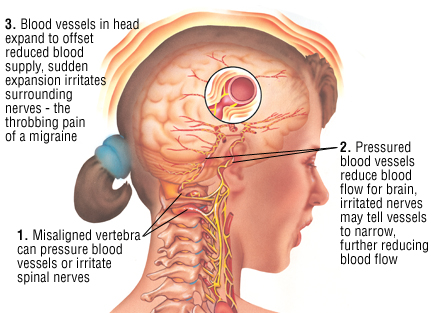
What are migraines?
Migraines are a recurring type of headache. They cause moderate to severe pain that is throbbing or pulsing. The pain is often on one side of your head. You may also have other symptoms, such as nausea and weakness. You may be sensitive to light and sound.
What causes migraines?
Researchers believe that migraine has a genetic cause. There are also a number of factors that can trigger a migraine. These factors vary from person to person, and they include
-
- Stress
- Anxiety
- Hormonal changes in women
- Bright or flashing lights
- Loud noises
- Strong smells
- Medicines
- Too much or not enough sleep
- Sudden changes in weather or environment
- Overexertion (too much physical activity)
- Tobacco
- Caffeine or caffeine withdrawal
- Skipped meals
- Medication overuse (taking medicine for migraines too often)
Some people have found that certain foods or ingredients can trigger headaches, especially when they are combined with other triggers. These foods and ingredients include
-
- Alcohol
- Chocolate
- Aged cheeses
- Monosodium glutamate (MSG)
- Some fruits and nuts
- Fermented or pickled goods
- Yeast
- Cured or processed meats
Who is at risk for migraines?
About 12% of Americans get migraines. They can affect anyone, but you are more likely to have them if you
-
- Are a woman. Women are three times more likely than men to get migraines.
- Have a family history of migraines. Most people with migraines have family members who have migraines.
- Have other medical conditions, such as depression, anxiety, bipolar disorder, sleep disorders, and epilepsy.
What are the symptoms of migraines?
There are four different phases of migraines. You may not always go through every phase each time you have a migraine.
-
- Prodome. This phase starts up to 24 hours before you get the migraine. You have early signs and symptoms, such as food cravings, unexplained mood changes, uncontrollable yawning, fluid retention, and increased urination.
- Aura. If you have this phase, you might see flashing or bright lights or zig-zag lines. You may have muscle weakness or feel like you are being touched or grabbed. An aura can happen just before or during a migraine.
- Headache. A migraine usually starts gradually and then becomes more severe. It typically causes throbbing or pulsing pain, which is often on one side of your head. But sometimes you can have a migraine without a headache. Other migraine symptoms may include
- Increased sensitivity to light, noise, and odors
- Nausea and vomiting
- Worsened pain when you move, cough, or sneeze
- Postdrome (following the headache). You may feel exhausted, weak, and confused after a migraine. This can last up to a day.
Migraines are more common in the morning; people often wake up with them. Some people have migraines at predictable times, such as before menstruation or on weekends following a stressful week of work.
How are migraines diagnosed?
To make a diagnosis, your health care provider will
-
- Take your medical history
- Ask about your symptoms
- Do a physical and neurological exam
An important part of diagnosing migraines is to rule out other medical conditions which could be causing the symptoms. So you may also have blood tests, an MRI or CT scan, or other tests.
How are migraines treated?
There is no cure for migraines. Treatment focuses on relieving symptoms and preventing additional attacks.
There are different types of medicines to relieve symptoms. They include triptan drugs, ergotamine drugs, and pain relievers. The sooner you take the medicine, the more effective it is.
There are also other things you can do to feel better:
-
- Resting with your eyes closed in a quiet, darkened room
- Placing a cool cloth or ice pack on your forehead
- Drinking fluids
There are some lifestyle changes you can make to prevent migraines:
-
- Stress management strategies, such as exercise, relaxation techniques, and biofeedback, may reduce the number and severity of migraines. Biofeedback uses electronic devices to teach you to control certain body functions, such as your heartbeat, blood pressure, and muscle tension.
- Make a log of what seems to trigger your migraines. You can learn what you need to avoid, such as certain foods and medicines. It also help you figure out what you should do, such as establishing a consistent sleep schedule and eating regular meals.
- Hormone therapy may help some women whose migraines seem to be linked to their menstrual cycle
- If you have obesity, losing weight may also be helpful
If you have frequent or severe migraines, you may need to take medicines to prevent further attacks. Talk with your health care provider about which drug would be right for you.
Certain natural treatments, such as riboflavin (vitamin B2) and coenzyme Q10, may help prevent migraines. If your magnesium level is low, you can try taking magnesium. There is also an herb, butterbur, which some people take to prevent migraines. But butterbur may not be safe for long-term use. Always check with your health care provider before taking any supplements.
Anyone who has experienced the pain of migraine is well aware that the declaration.
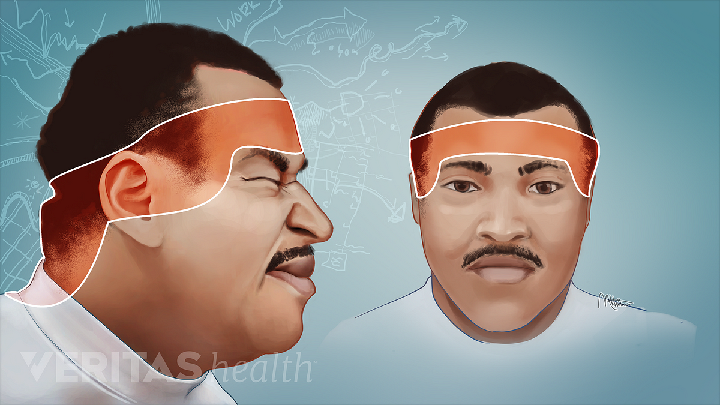
Often with one side of the head, these headaches can be very stressful for patients. They are able to be offended, but also painful to the point where you just throw up. The effects can last from 12 to 72 hours, with little relief or not.
Many people experience an aura at the beginning of a migraine. “Lightning” in the corner of my eye, dizziness, blurred or double vision and nausea were observed, are some of the classic tale signs that a migraine is to occur. The pain is extreme, and it is extremely sensitive to sights and sounds. Light of any kind is intolerable. The individual will need to lie as a rule, in a dark and quiet, although they too are waiting for the disappearance of these headaches.
Many women begin to experience migraines because they go through menopause.
You can never find a headache in their lives, but they are steadily during this period. There is no known reason, why would they start to happen in this time of life. Often, the trigger voltage is used, but may at some point this individual will be brought to eat. Physical illness may be an additional trigger, but it is not known, for an individual.
There are migraine drugs to prevent or relieve symptoms after the accident. Many people find themselves in the emergency room of the hospital, as they always have a shot if a migraine is severe enough. Signs and symptoms of visual impairment due to extreme headaches accompanied lead people to think about what they can to have a brain tumor. Your doctor will probably order an MRI to know for this purpose. Governance
even though you suffer from frequent migraines to stretch and use a cold compress on the forehead and back of neck. Caffeine will also help relieve signs and symptoms of dilated blood vessels.
Often a doctor will prescribe certain drugs that are also used to make the higher blood pressure because they have an influence on the frequency and intensity of migraines seem to possess. Known as calcium channel blockers and beta blockers have been used with some success in the past. These are used as preventative measures.
Your doctor will work with you to try to alleviate the frequency of migraine, although some people have more or as much as 5 or 6 in the week. How often you have it, is not something that can be predicted.
Try to determine what it is you need to make simple, took place before the headache. Keep a list of things you eat that appear to precipitate migraine. My doctor informed of your findings are.
Help with the discovery of what is the cause of migraine to control them. even though the natural way does not control the migraines, you will find drugs on the market these days, a doctor can prescribe to help with migraines can be. It always says if you can control them without medication, then it is proposed to do.
Why is Fioricet used to treat migraine?
Fioricet is an older medication that used to frequently be prescribed to treat migraine symptoms. However, there is not enough evidence that shows it’s effective for migraine attacks, especially when compared to safer products.
Although Fioricet has been used for many years for migraine, it’s not approved for this use, and there are greater risks than benefits with this medication.
Fioricet may be an option if other migraine treatment options have not worked. Your doctor will just want to monitor you closely to avoid side effects.
It’s prescribed to help relieve immediate headache symptoms, but not to prevent migraine attacks.
How does Fioricet work to treat migraine?
Fioricet contains three different active ingredients which work together on tension headaches. The exact way Fioricet works to help relieve tension headache is not clear.
Butalbital is a barbiturate that helps with relaxation and anxiety, acetaminophen works as an analgesic for pain relief, and caffeine also helps with pain relief.
How do you take Fioricet?
Fioricet is available as a capsule you take by mouth. The recommended dose is 1-2 capsules every 4 hours. Do not take more than 6 capsules in a 24-hour period.
Fioricet can cause an upset stomach, so taking it with food or milk may help.
Ask your pharmacist for information on the best way to take Fioricet.
What are the possible side effects of taking Fioricet?
Share your medical history with your doctor and ask if Fioricet is safe for you to take. Fioricet can cause some serious side effects, including:
-
-
- confusion
- seizure
- depression
- drowsiness, dizziness
- feeling intoxicated
- stomach pain
- dry mouth
- heartburn
- fast heart rate
- muscle pain
- rash, itching
- vomiting
-
If you experience a severe or life-threatening reaction to Fioricet, call 911 right away.
Mayne Pharma
Pill Identification: MIA 110
Potential drug interactions from Fioricet
Fioricet can also interact with different medications, including:
-
-
- MAO inhibitors
- opioid pain relievers
- alcohol
- sleep or anxiety medications like benzodiazepines
- other medications that cause sedation
- multi-symptom cough/cold medications with acetaminophen
-
This is not a full list of all the side effects and interactions of Fioricet. Ask your pharmacist for a complete list.
Are there risks from taking Fioricet for migraine?
Fioricet has several risks and may not be suitable for everyone.
The active ingredient butalbital in Fioricet may be habit-forming. Using higher doses for a long time may lead to dependence on Fioricet. Suddenly stopping the medication after regular use may also cause withdrawal symptoms.
Drinking alcohol or taking other sedative medications with Fioricet may be harmful and cause dangerous side effects. Butalbital takes a long time to clear from your body.
Do not take Fioricet with other products that have the same active ingredients. Taking too much of these ingredients together can increase the risk of overdose, cause liver or kidney damage, and may be life-threatening.
Talk with your doctor about any medications and over-the-counter products you’re taking, including vitamins, herbs, and natural supplements.
Some examples include:
-
-
- acetaminophen (Tylenol, multi-symptom cough/cold products)
- caffeine (energy drinks, Excedrin migraine, caffeine pills)
- butalbital (barbiturates)
-
Taking Fioricet regularly can increase your risk for rebound headaches or medication overuse headaches. The American Migraine Prevalence and Prevention Study found use of butalbital for 5 days per month would increase the risk of acute migraine becoming chronic migraine.
Fioricet can raise blood pressure and heart rate, if you have a history of high blood pressure or heart related conditions, ask your doctor about the risks of Fioricet.
