The symptoms of fibromyalgia include pain and tenderness throughout the body that is often associated with other conditions that reduce a person’s ability to function and affects her quality of life. People with fibromyalgia often have difficulty sleeping, feel tired during the day, and experience irritability and depression, all of which can affect their life at work and at home.
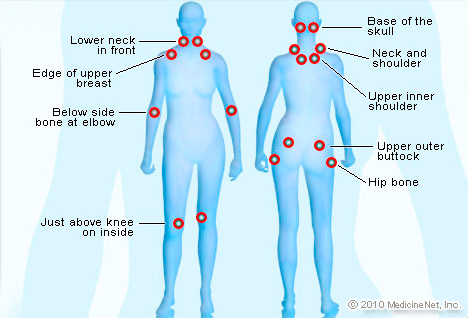
Between 1 percent to 5 percent of adults in the U.S. have fibromyalgia, with women much more likely to develop it than men—about 80 to 90 percent of fibromyalgia sufferers are women. It can strike children and teens, but it’s more common in older adults, with most cases occurring between the ages of 40 and 70.
Because there is not a single, specific cause of fibromyalgia and the symptoms can vary from patient to patient, choosing an effective treatment can be challenging. Experts say the best, overall strategy includes medications and nondrug therapies, such as exercise, counseling, and stress relief.
The medications used to treat fibromyalgia includeantidepressants (amitriptyline, nortriptyline, fluoxetine, paroxetine, duloxetine, milnacipran), a few anti-seizure medications (gabapentin, pregabalin), and a muscle relaxant (cyclobenzaprine). But studies show that the benefits of these medications are generally small. There is no clear evidence that one drug is better than another, and all of them probably lose their benefit over time.
Each drug differs in the risks it poses to you. All antidepressants should be used with caution in those with a history of suicide attempt or who are at risk of suicide, especially in people 25 years old or younger. Amitriptyline, cyclobenzaprine, gabapentin, and pregabalin all cause increased sedation and should be used with caution in the elderly.
The medications differ substantially in price, so cost might be an important factor in determining which one you choose. The monthly cost for these drugs ranges from as little as $6 to more than $500. Taking into account the evidence of their effectiveness and safety as well as their price, we have chosen three Consumer Reports Best Buy Drugs as initial options to consider if you and your doctor have decided that a medication is appropriate for your fibromyalgia symptoms:
- Generic amitriptyline
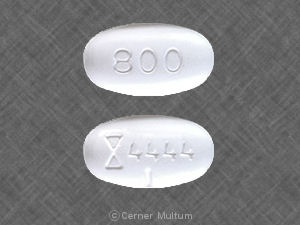
- Generic gabapentin
- Generic paroxetine-IR (immediate release)
All of these medications have been on the market for 15 years or more and have been widely used. They are all available as inexpensive generics and are at least as effective and safe as the other fibromyalgia medications.
Although side effects of sedation, dry mouth, and dizziness are common, serious side effects are rare.
Gabapentin and pregabalin are classified as antiseizure medications, but they are also used to help relieve pain in people with fibromyalgia. Both medications alter the brain chemistry. Pregabalin decreases levels of chemicals in the brain called neurotransmitters that build up because of the constant firing of the nerves in the spinal cord and the brain. It also increases other neurotransmitters that help suppress the constant firing of the nerves, which helps relieve pain. It’s unclear which neurotransmitters are affected by gabapentin or pregabalin.
Both drugs improve pain, sleep, fatigue, and the quality of life in people with fibromyalgia to about the same degree as amitriptyline. In clinical trials, 70 percent of people with fibromyalgia who took gabapentin for 12 weeks said they felt better compared with 40 percent of those who took a placebo. In addition, 51 percent of those who took gabapentin experienced a reduction of one-third in their pain compared with those who took a placebo.
In another trial, between 40 percent and 80 percent of people who took pregabalin said their pain was reduced by nearly a third, compared with 28 percent to 38 percent of those who took a placebo. For doses of 300 mg to 600 mg per day of pregabalin, 20 percent to 24 percent of patients said their pain was reduced by half compared with 12 percent of patients taking placebo.
One of the most common side effects of pregabalin and gabapentin is sedation. This is why they are often given at higher doses at night, which seems to help with sleep. Other side effects can include confusion, blurred vision, dizziness, liver and kidney impairment, and problems with concentration. In particular, they should be used with caution in elderly people due to side effects of confusion, dizziness, and sedation. Both drugs can also cause swelling, so people with heart failure should not take them. Gabapentin has been shown to increase the risk of suicide in depressed people and should be avoided in those at increased risk of suicide attempt.
Above report is from http://www.consumerreports.org/cro/2014/02/evaluating-prescription-drugs-used-to-treat-fibromyalgia/index.htm
