The esophagus is the tube that carries food, liquids and saliva from your mouth to the stomach. You may not be aware of your esophagus until you swallow something too large, too hot or too cold. You may also become aware of it when something is wrong.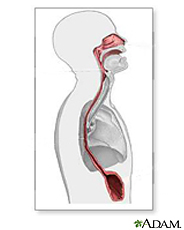
The most common problem with the esophagus is gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD). It happens when a band of muscle at the end of your esophagus does not close properly. This allows stomach contents to leak back, or reflux, into the esophagus and irritate it. Over time, GERD can cause damage to the esophagus. Other problems include heartburn and cancer.
Treatment depends on the problem. Some get better with over-the-counter medicines or changes in diet. Others may need prescription medicines or surgery.
Certainly. Here’s a comprehensive and detailed overview of esophagus disorders—covering types, causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatments.
🔹 What Is the Esophagus?
The esophagus is a muscular tube (~25–30 cm) connecting the throat (pharynx) to the stomach. Its main role is to move food and liquids to the stomach through a process called peristalsis (coordinated muscle contractions). Disorders of the esophagus interfere with swallowing, digestion, or esophageal function.
🔹 Major Esophageal Disorders
1. Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD)
Definition:
Chronic condition where stomach acid or contents flow back into the esophagus (acid reflux), irritating its lining.
Causes:
- Weak or dysfunctional Lower Esophageal Sphincter (LES)
- Obesity
- Hiatal hernia
- Smoking, alcohol
- Certain medications
Symptoms:
- Heartburn (burning chest pain)
- Regurgitation
- Chronic cough, sore throat
- Hoarseness
- Dysphagia (difficulty swallowing)
Diagnosis:
- Endoscopy
- 24-hour pH monitoring
- Esophageal manometry
- Barium swallow X-ray
Treatment:
- Lifestyle changes: Avoid acidic foods, lose weight, elevate head of bed
- Medications:
- Antacids (e.g., Tums)
- H2 blockers (e.g., ranitidine)
- Proton pump inhibitors (PPIs) (e.g., omeprazole)
- Surgery (e.g., Nissen fundoplication) in severe or refractory cases
2. Esophagitis
Definition:
Inflammation of the esophagus, often caused by acid reflux, infections, medications, or allergies.
Types:
- Reflux esophagitis – from GERD
- Infectious esophagitis – often in immunocompromised patients (Candida, HSV, CMV)
- Eosinophilic esophagitis (EoE) – allergic condition involving white blood cells
- Pill-induced esophagitis – from medications lodging in the esophagus (e.g., doxycycline, bisphosphonates)
Symptoms:
- Painful swallowing (odynophagia)
- Chest pain
- Nausea
- Heartburn
- Food impaction
Diagnosis: Endoscopy with biopsy
Treatment:
- Treat underlying cause (acid suppression, antifungals, steroids)
- Avoid trigger foods or medications
3. Esophageal Stricture
Definition:
A narrowing of the esophagus, usually from chronic inflammation and scarring.
Common Causes:
- Long-standing GERD
- Radiation therapy
- Ingestion of corrosives (alkali or acid)
- Surgery or intubation trauma
Symptoms:
- Progressive dysphagia (first to solids, later to liquids)
- Regurgitation
- Weight loss
Diagnosis: Endoscopy, barium swallow
Treatment:
- Endoscopic dilation (balloon or bougie)
- PPI therapy to prevent recurrence
- Surgery for complex or recurrent strictures
4. Achalasia
Definition:
A rare motor disorder where the lower esophageal sphincter fails to relax and peristalsis is absent, causing food to get stuck.
Causes:
- Idiopathic degeneration of nerve cells in esophageal wall
- Chagas disease (Trypanosoma cruzi infection)
Symptoms:
- Difficulty swallowing both solids and liquids
- Regurgitation of undigested food
- Chest pain or pressure
- Weight loss
Diagnosis:
- Esophageal manometry (gold standard)
- Barium swallow (shows “bird-beak” appearance)
- Endoscopy
Treatment:
- Botulinum toxin injection (temporary)
- Pneumatic dilation
- Surgical myotomy (Heller)
- Peroral endoscopic myotomy (POEM)
5. Esophageal Cancer
Types:
- Squamous cell carcinoma – associated with smoking, alcohol, poor nutrition
- Adenocarcinoma – often arises from Barrett’s esophagus (a complication of GERD)
Risk Factors:
Symptoms:
- Progressive dysphagia (solids → liquids)
- Unintentional weight loss
- Chest pain
- Hoarseness
- Coughing
Diagnosis:
- Endoscopy with biopsy
- CT or PET scan for staging
Treatment:
- Surgery (esophagectomy)
- Chemotherapy & radiation
- Targeted therapy/immunotherapy
- Palliative stenting in advanced disease
6. Barrett’s Esophagus
Definition:
A condition in which chronic acid exposure causes abnormal changes in the esophageal lining, increasing cancer risk.
Cause: Long-standing GERD
Diagnosis: Endoscopy with biopsy (intestinal metaplasia)
Treatment:
- PPIs to control acid
- Regular surveillance (biopsies)
- Ablation or endoscopic resection for high-grade dysplasia
7. Esophageal Varices
Definition:
Dilated veins in the esophagus, often due to portal hypertension from liver cirrhosis. Risk of massive bleeding if ruptured.
Symptoms:
- Vomiting blood (hematemesis)
- Black tarry stools (melena)
- Shock (if bleeding is severe)
Diagnosis:
- Endoscopy
- Blood tests (for liver function, anemia)
Treatment:
- Endoscopic band ligation
- Beta blockers (non-selective) to lower portal pressure
- TIPS (Transjugular Intrahepatic Portosystemic Shunt)
- Emergency management with IV fluids, blood transfusions, octreotide
8. Dysphagia (Swallowing Difficulty)
Categories:
- Oropharyngeal dysphagia: Problem initiating swallowing (e.g., neurological)
- Esophageal dysphagia: Problem in the esophagus itself (stricture, cancer, achalasia)
Evaluation Tools:
- Barium swallow
- Endoscopy
- Manometry
Management: Depends on underlying cause (mechanical, neurological, inflammatory, etc.)
🔹 Diagnostic Tools Summary
| Test | Use |
|---|---|
| Endoscopy (EGD) | Direct visualization, biopsy |
| Barium swallow | Structural abnormalities, motility issues |
| Manometry | Esophageal pressure and muscle function |
| 24-hour pH monitoring | Acid reflux diagnosis |
| Biopsy | Detect inflammation, Barrett’s, cancer |
🔹 Summary Chart
| Disorder | Main Symptom | Key Feature | Treatment |
|---|---|---|---|
| GERD | Heartburn | Acid reflux | PPIs, lifestyle |
| Esophagitis | Painful swallowing | Inflammation | Treat cause |
| Stricture | Dysphagia | Narrowing | Dilation |
| Achalasia | Solids & liquids stuck | LES fails to relax | Myotomy, dilation |
| Barrett’s | Often asymptomatic | Precancerous | Monitor, ablation |
| Cancer | Progressive dysphagia | Mass lesion | Surgery, chemo |
| Varices | Bleeding | Portal hypertension | Banding, beta blockers |
If you’d like, I can provide illustrations, diagnostic flowcharts, or a printable summary. Would you like to explore one of these disorders in more depth?
